
Anal sac disease results from infected or inflamed anal glands and can be very painful for a cat. When the anal glands do not routinely release their fluid, the buildup can cause symptoms like thick secretions, foul odor, and blood in the stool. Anal sac disease can result from various factors that make a cat unable to expel its anal fluid, including soft stools, tumors, and obesity. A vet will diagnose anal sac disease using a physical examination and diagnostic tests. Sometimes, the only necessary treatment is a manual expression by a vet, but the condition can require surgery. The prognosis for treated cats is good but untreated anal sac disease can cause other health problems. You can work to prevent anal sac disease by regularly monitoring your cat's rectum.
Anal sac disease occurs when the anal glands, the two small balloon-like structures that release fluid on either side of a cat's rectum, become inflamed or infected. Anal sacs function like a skunk's scent glands and release territory-marking odor. Anal sacs are located just under the skin's surface and have tiny ducts that connect the sac to the rectum. When the sacs become inflamed, they don't correctly secrete, and fluid builds up and can lead to rupture. Fluid buildup from the anal sacs can thicken into a noticeable, dark, foul-smelling paste. If not expressed routinely during defecation or manually by your veterinarian, the anal sacs can foster bacteria and become engorged and very painful. Anal sac disease can result from a variety of conditions.
Symptoms of anal sac disease are very uncomfortable for your cat. If you notice an abnormality near your cat's anus, visit your vet right away.
At first, anal sac diseases will first cause minor discomfort, including anal gland fluid on surfaces, and a foul odor. As the condition worsens, your cat may cry in pain when defecating, and blood may appear in the feces. Excessive licking or biting at the rectal opening or general hind end area signify discomfort, and your cat may scoot in an effort to relieve the pain that precedes a rupture. A ruptured anal sac is relatively rare but incredibly painful, and a cat typically cries as the additional hole next to the rectum opens and bleeds.
If anal sacs do not express as a cat defecates, infection will occur due to bacterial buildup and inflammation. Various causes can prevent anal glands from expressing.
To diagnose anal sac disease, your veterinarian will perform a physical examination on your cat, focusing on the rectum. If a tumor is suspected, your vet will perform additional tests. Because anal sac disease shares clinical signs with parasitic infections, your vet may run a fecal flotation test to rule out other diagnoses.
If the anal sacs are impacted, they will need to be drained. This may be able to be done by your vet physically squeezing the sacs or may require a surgical incision. Never attempt to drain the anal sacs at home. Reparative or removal surgery is necessary if the anal sac has ruptured or abscessed. Your vet will likely prescribe antibiotics, pain medications, and a specialized diet during your cat's recovery.
The best preventative measure against anal sac disease is close monitoring of your cat's bowel movements and rectal health. Additionally, obesity contributes to developing anal sac disease, so maintaining a healthy lifestyle for your cat is essential in preventing anal sac disease. Probiotics, prebiotics, and fiber can help keep feces firm and promote natural sac expression.
The prognosis is good for cats that have been treated for anal sac disease. Infection usually doesn't recur but is possible in obese cats. If your cat isn't treated, the disease can cause secondary infection or cancer. Following surgery, your cat may suffer from incontinence, but this usually quickly resolves itself.
Anal sacs function as territory markers or predator repellants. Domestic cats don't need anal sacs, therefore their removal doesn't negatively impact a cat.
Anal sac secretions usually smell like rotten fish, rancid cheese, or metallic. You'll likely be able to recognize the foul odor from its intensity.
If treated, anal sac disease is not at all fatal, and usually doesn't recur. However, if untreated, it can lead to complications and other illness.

Everything You Need to Know About Raising Your First Cat
Whether you are thinking about getting a cat or just adopted your first one, these are the things to know to make your relationship a lasting one.
8 Ways To Help Your Cat Lose Weight
Cats who are at a healthy weight are happier, more agile, and tend to live longer. Here are 8 tips for managing a cat weight loss programme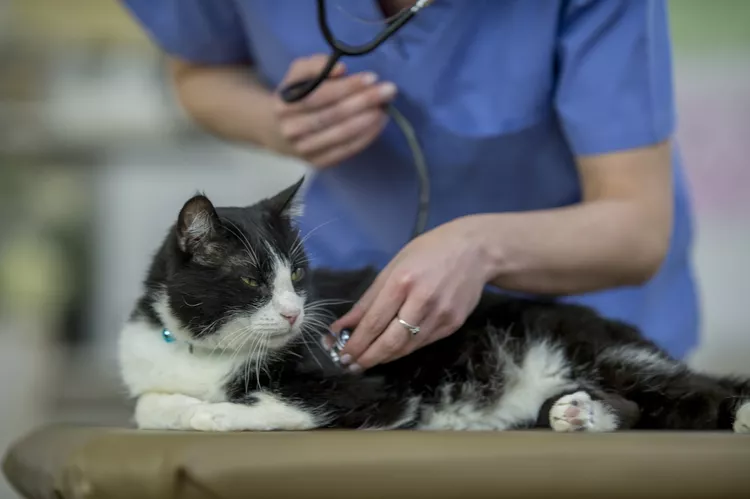
Heart Disease in Cats
Like humans, cats can get heart diseases that may lead to serious problems. Learn all about symptoms along with the causes, treatment, and prevention.
Is Coconut Oil Safe for Cats?
Coconut oil is touted as a miracle food. Can coconut oil improve your cat's health? Is coconut oil even safe for cats?
Taurine for Cats
Taurine is an essential animal protein in your cat's diet. Learn more about the various ways it supports your feline's body.
Can Cats Eat Peanut Butter?
Peanut butter is not toxic to cats, but it might not be the best choice of treat for them.
Why Do Cats Stare at Walls?
Cats can have some quirky behaviors, including staring at walls. Why do cats do this and when should you be concerned?
Patellar Luxation in Dogs
If your dog has a knee that seems to pop out of place, it may have a patellar luxation. Find out what this means and what can be done about it.
13 Signs of Cancer in Dogs
The signs of cancer in dogs may include lumps and bumps, lethargy, vomiting, diarrhea, pain, abdominal swelling, and more. Signs may be mild or obvious depending on the type of cancer and its severity. Learn common signs of cancer in dogs so you’ll know when to call the vet.
Ear Mites in Puppies and Dogs
Ear mites can be a big discomfort for puppies and dogs. Learn about the causes, treatment, and prevention to keep mites away from your pets.
Why Do Dogs Eat Dirt?
Some dogs eat some strange things. What does it mean if your dog eats dirt and when should you be concerned?
200 Tortoiseshell Cat Names for Your Bi-Colored Kitty
Tortoiseshell cats are a rare phenomenon and deserve a fitting name. We've pulled together 200 tortoiseshell cat names, including male names, female names, cute names, and names inspired by their coat color and pattern.
How to Manage Your Cat's Claws
Here are ways you can help your cat maintain healthy claws while protecting your furniture at the same time.
Hair Loss in Cats
Hair loss in cats is a common problem with many possible causes. Learn the causes, treatments, and prevention of hair loss in cats, also known as alopecia.
Neurological Disorders in Cats
Neurological disorders in cats range from minor to serious. Any neurological condition is a major disruption to your cat's central nervous system. Learn the causes, treatment, and prevention of neurological disorders in cats.
Hair Loss on Hind Legs in Cats
Cats experience hair loss on their hind legs for a variety of reasons. Learn about potential causes, treatments, and ways to prevent it.
Can Cats Have Milk? Why They Really Shouldn’t Drink The Stuff
Despite what we’ve learned from pop culture, cats shouldn’t drink milk as most cats are lactose intolerant. Learn more about feeding milk to cats and alternatives you can feed your cat instead.
Can Cats Eat Dog Food?
Can cats eat dog food? In small amounts, it's unlikely to be a problem, but long-term feeding of dog food to cats can cause health issues and malnutrition.
Why Some Black Cats Look Different in the Sun
Some black cats look different in the sunlight. Whether it's cat genetics, a mutation, or a summer "rust," learn why they appear to have another coat.
Training Your Fearful Cat to Be Confident
Cats can become scared for any number of reasons. Learn about techniques that can help your fearful cat and reduce its anxiety so kitty lives a happy life.